A Write-Up For Soc Analyst Training CTFs - Part 1
Competition
Special kind of cybersecurity competition designed to challenge its participants to solve computer security problems.
🚩 Flag
CTFCVE Number
What is the CVE ID that is related to EternalBlue
Flag Format: XXX-XXXX-XXXX
💡 EternalBlue :
EternalBlue is a Microsoft exploit created by the US National Security Agency (NSA). Officially named MS17-010 by Microsoft — EternalBlue exploits a vulnerability in Microsoft’s implementation of the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and gave the US NSA backend access to devices running Windows operating systems like Windows XP and Windows 7.
A quick google search gives us CVE ID that is related to EternalBlue.
🚩 Flag
CVE-2017-0144Smart Role
skills of collecting information out of cyberspace that has been previously analysed and shared between organisations about different attack scenarios and vectors.What is the role name of the above definition
🚩 Flag
flag{threat intelligence}Backdoor
Challenge Link
Our server compromised due to known vulnerability introduced from many years, Kindly check and identify this flow:
X: Attack source → EX. “Internal/External”
Y: The Source IP → x.x.x.x
Z: CVE Num of the attack → xxx
W: Destination Mac Address
Flag format: flag{X:Y:Z:w}
💡 Solution
Let’s download the pcap file for further analysis to answer the questions. We will use Wireshark in this task.
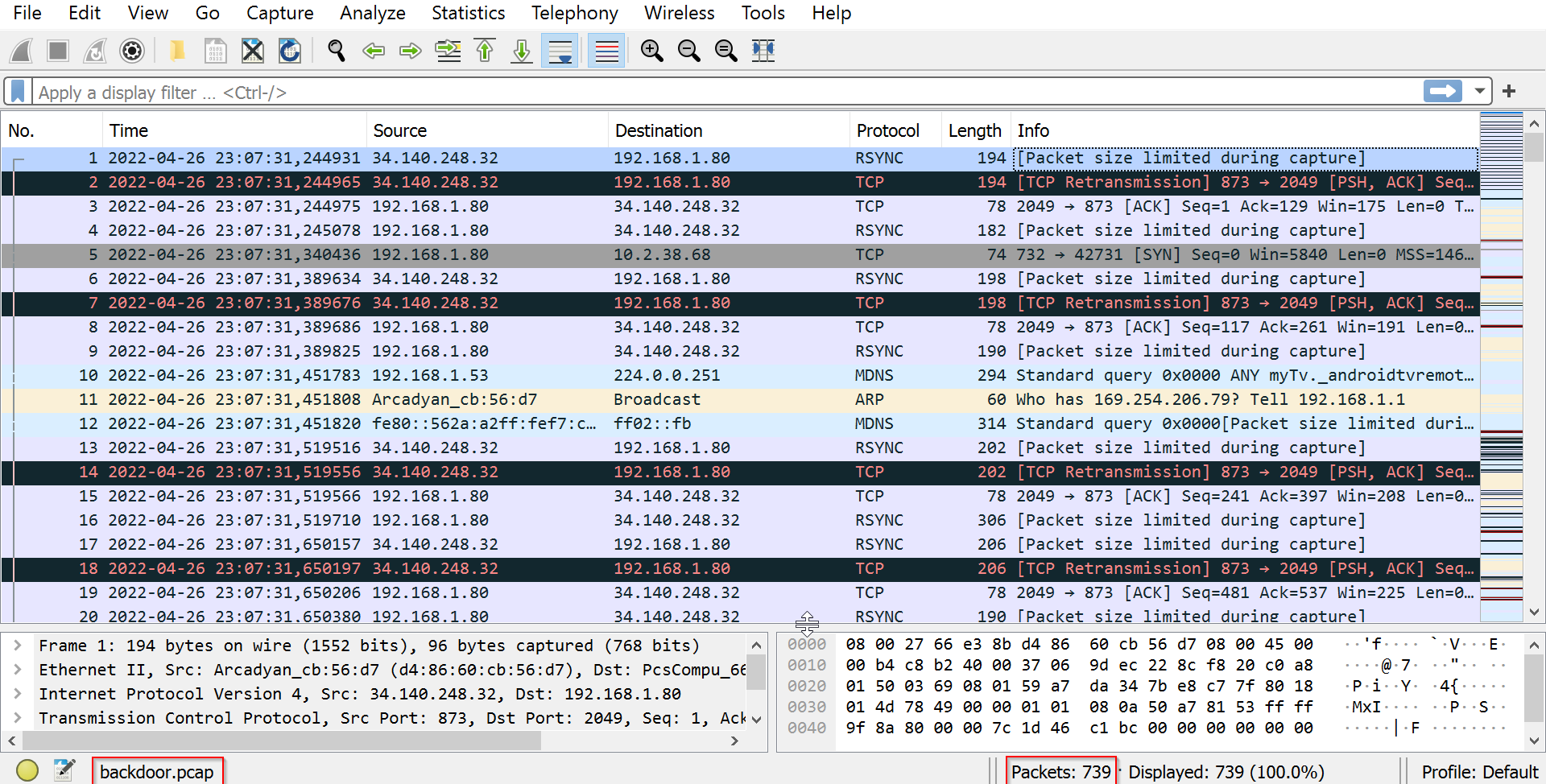
We have 739 packets in total as shown in the screenshot below :
 |
|---|
| Total Packets |
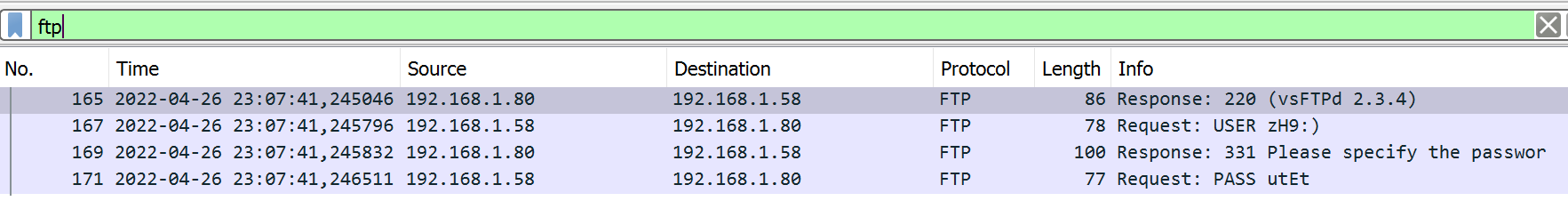
I applied an HTTP filter but no packet is displayed so I tried FTP filter and I found 4 packets :
 |
|---|
| FTP Packets |
The first request shows an important hint which is vsFTPD 2.3.4. I did a google a search and I found that vsFTPD 2.3.4 (stands for “Very Secure FTP Daemon”) is a vulnerability presented in Linux FTP service and was exploited by adding a malicious backdoor to the VSFTPD download archive.
The CVE ID that is related to vsFTPD 2.3.4 is CVE-2011-2523.
The packets also shows the source IP address : 192.168.1.58 and it’s an internal IP.
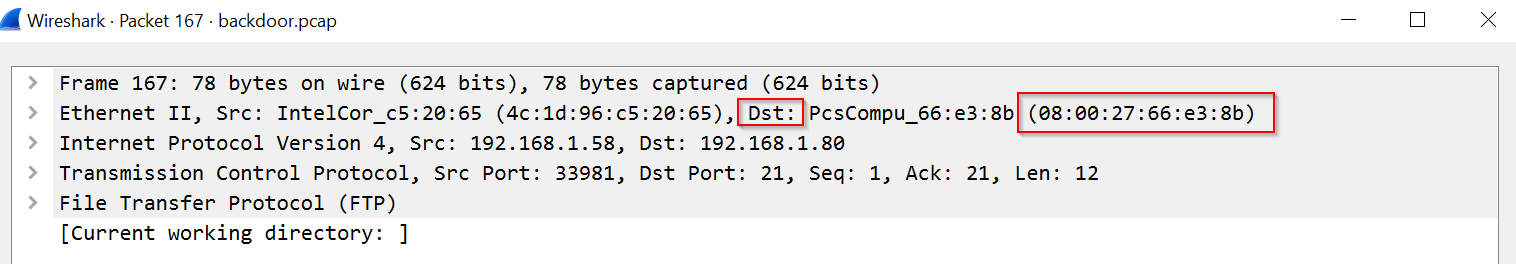
Last thing to figure out is the destination MAC address associated with destination IP address 192.168.1.80 :
 |
|---|
| Destination MAC Address |
Now we have all the flag answers.
🚩 Flag
flag{internal:192.168.1.58:CVE-2011-2523:08:00:27:66:e3:8b}Creepy DNS
Challenge Link
Our NMS detect a suspected traffic, your task is to investigate the captured traffic and find the anomaly reason.
💡 Solution
Let’s download the pcap file and open it with wireshark.
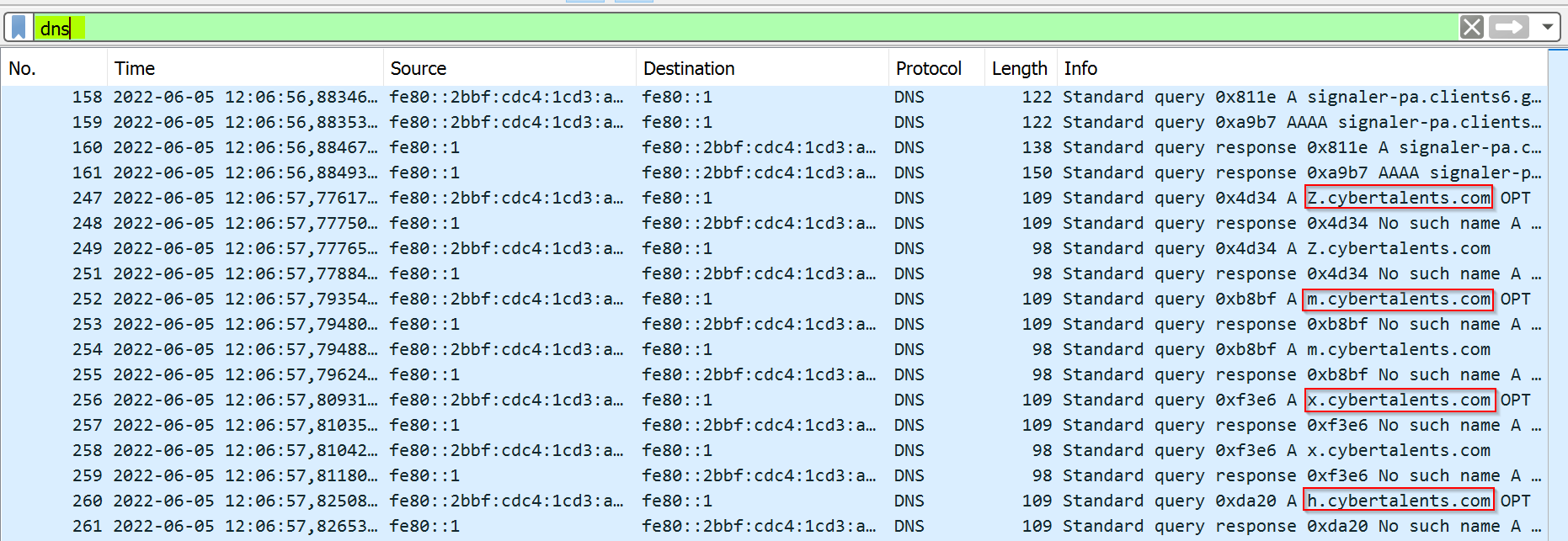
The pcap file has 683 packets in total and since the challenge is about DNS, I will apply DNS protocol as a filter to get the following result :
 |
|---|
| DNS Filter |
Notice that there are many subdomaisn of cybertalents that starts with a strange letter (ex: Z.cybertalents, m.cybertalents, x.cybertalents …). I will use Tshark to collect the first letter of each subdomain to see what I can get.
 |
|---|
| Tshark Filter |
I used the following Tshark command : tshark -r dns.pcapng |grep -E -o "[a-zA-Z0-9].cybertalents.com" |cut -d "." -f 1|uniq| tr -d "\n" and the result seems to be a base64 encoded text.
💡 Tshark Command Line Options:
- -r : Read packet data from dns.pcapng file
- -o : –only-matching which means print only the matched (non-empty) parts of a matching line
- -d : use “.” as field separator or delimiter
And finally the tr -d to delete the \n character so all the first letters will be concatenated.
I will decode the text string to get the flag :
 |
|---|
| Base64 Decode |
🚩 Flag
flag{tshArk_Is_Awes0me_Netw0rking_to0l}Beans Detector
You have received the alert in your company WAF that web attack happened recently. Please check and identify the below details :
X : Attacker IP
Y : Name of Vulnerability Scanner used by the Attacker
Z : number of bytes in the sensitive files Leaked
W : Date and time of the Sucessful attack (xx/xx/xxxx:xx:xx:xx)
Flag format: flag{X:Y:Z:w}
💡 Solution
I downloaded the log file and open it in my virtual machine for further investigation :
 |
|---|
| Log Content |
Since they mention some sensitive files in the challenge description, I will use look for any flag file or string using grep command line :
 |
|---|
| grep command line |
I got the flag.txt request and now we can answer the questions :
Attacker IP is 172.17.0.1 and he/she used the Wfuzz tool as a vulnerability scanner. The number of bytes of sensitive files that was leaked is 49 bytes as shown in the first line (first request) in the previous screenshot using grep and finally the attack was performed in 12/Jun/2022:11:05:12
🚩 Flag
flag{172.17.0.1:wfuzz:49:12/06/2022:11:05:12}Pass reset
Challenge Link
You have received the email below, Please examine the email and answer the below questions :
X : The sender mail ID
Y : The date that user received the email (DD/MM/YYYY)
Z : The domain name of associated URL on mail body (ABC.com)
W : Do you think this email more likely to be legitimate or suspicious, add L for legitimate or S for suspicious.
Flag format: flag{X:Y:Z:w}
💡 <h3>Solution</h3>
I extracted the file with password “infected” and open it with this online message viewer
 |
|---|
| Email displayed |
To answer the previous question, we need to open the message file with notepad for more details:
- The sender email address is found in the
Fromfield : roger@captech.com - Date of email reception : Fri, 25 Feb 2022
- The domain name of associated URL on mail body : to find out this domain, I will decode the message body to see the related URL :
 |
|---|
| Email Body base64 encoded |
Email after base64 decoding :
 |
|---|
| Email Body base64 decoded |
In the mail body we can see the phishing link after decoding the message.
- For the last question I used VirusTotal by checking the phishing link to decide if the email is legitimate or suspicious :
 |
|---|
| Link Verification with VirusTotal |
The Link is malicious, thus the email is suspicious!
🚩 Flag
flag{roger@captech.com:25/02/2022:attemplate.com:S}
![]()
“To beat a hacker, you have to think like a hacker” 💙