Learn more about SIEM solutions, their architecture and their functions.
What is SIEM?
SIEM which stands for security information and event managementa is a security solution that collects data from various endpoints/network devices across the network, stores them at a centralized place, and performs correlation on them.
These data that are collected and correlated will be analyzed to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach or potential threat.
Potential threats detected with SIEM are reviewed by SOC analysts.
SIEM Architecture
In this part we will explain the different part of SIEM architecture, how SIEM systems are built, how they go from raw event data to security insights, and how they manage event data on a huge scale.
Log Collection
The log collection is one of the most important parts of SIEM architecture because without these logs our SIEM tool would be useless.
💡 But what is Log ?
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. In the simplest case, messages are written to a file, called a log file.Alternatively, the messages may be written to a dedicated logging system or to a log management software, where it is stored in a database or on a different computer system.
source: Wikipedia
So Log files are a historical record of everything and anything that happens within a system, including events such as transactions, errors and intrusions.
💡 Logs collections within SIEM
At this point, SIEM systems collect and analyze security data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, and applications. The SIEM can collect data in two ways:
- Agent Based : Agent-based log collection tends to be the default choice. Despite being a specialized application, the agent has multiple functions. It not only collects and filters events, but it can also parse and convert the logs into other formats before forwarding. Syslog which is a network protocol is used for log transfers.
In order to implement this method, a log agent software is required on all devices. Beats and NXLog are examples of open source agents.
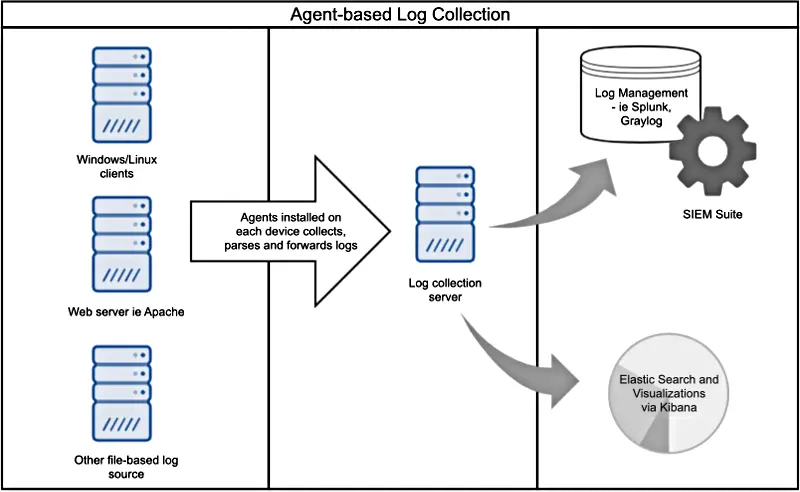 |
|---|
| Agent Based Log Collection |
Most SIEM Products have their own software agent. For example Splunk has a software agent called Uviversal Forwarder.
- Agenless : This option is adopted when deploying log collection agents may not be feasible for all required devices in an environment. In this method, logs are sent by the client, host, system or device by connecting to the target with SSH or WMI. In other words, devices send the logs to the servers.
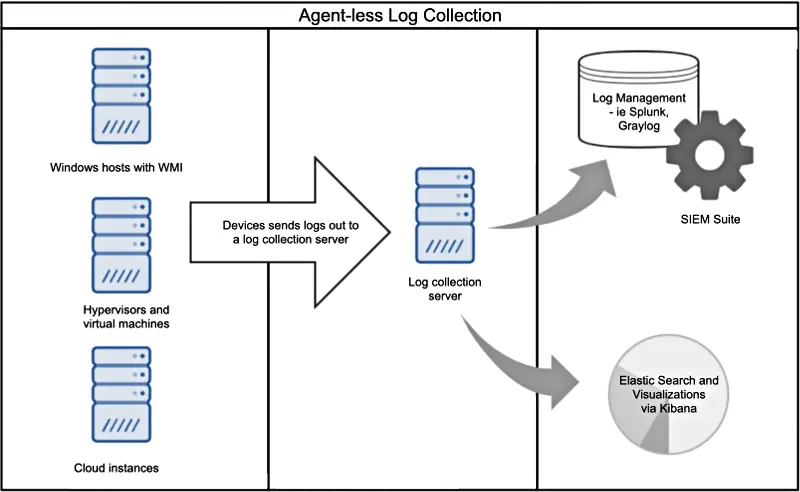 |
|---|
| Agentless Log Collection |
Log Aggregation
Log aggregation is collecting logs from multiple computing systems, parsing them and extracting structured data, and putting them together in a format that is easily searchable and explorable by modern data tools. This can be done in two different ways : push and pull method
- Push Method : Logs are pushed from source to server.
- Pull Method : Logs are pulled by server from source.
💡 log aggregator functions : The first place where the generated logs are sent is the log aggregator. We can edit the logs coming here before sending them to the destination. The log aggregator has the following functions :
- Filtering : For example, if we want to get only status codes from a web server logs, we can filter among the incoming logs and send only the desired parts to the target.
- Parsing : Parsing is the process of extracting key pieces of information from each logged event and putting them into a common format. These values are then stored for later analysis. Some common log formats include: JSON, CSV and Windows Event Log.
- Modification : Log modification can be useful in some cases when you need to edit the logs. For example, while the date information of most logs you collect comes in the format dd-mm-yyyy, if it comes from a single source as mm-dd-yyyy, you would want to convert that log. Or you may need to convert UTC + 2 incoming time information to UTC + 1.
- Enrichment : Log enrichment involves adding important information that can make the data more usefule and efficient to save time. An example of log enrichment is geolocation. The geolocation of the specified IP address can be found and added to the log. Thus, the person viewing the log saves time. It also allows you to analyze location-based behavior.
💡 EPS
EPS or events per second is the standard unit of measurement for log processing speed, (i.e how many events an application can process in one second). From siem perspective, EPS is a standard metric for evaluating log collection and management tools like NXLog software agent.
Log Storage
Now The next step is to store incoming logs for later retrieval. While many SIEM structures focus on storage size, it is very important to keep in mind that speed of data access is equally important as High-sized storag.
When we look at the popular storage technologies in the market (Example: mysql), we see that it is focused on adding, editing, and deleting data. But our focus is on indexing the data, we do not intend to edit the stored log later. Our purpose is to access data as quickly as possible. For this, WORM (Write Once Read Many) based technologies are more suitable to be used in SIEM.
Alerting and Notification
At this point, our logs are collected, processed and stored. Now, we need to detect abnormal behavior using the data we have and generate alerts. These alerts are generated when the system detects anomalous activity, such as failed login attempts, unauthorized access, or suspicious network traffic.
Creating alrets can be done in 3 different ways using whitelists, blacklists and long tail.
- Blacklist : A list of discrete entities that have been previously determined to be associated with malicious activity. For example, we can collect the prohibited process names (Example: mimikatz.exe) and write them to a list. Then, if a process in this list appears in the logs, we can create an alert.
- Whitelist : It operates on an ‘allow list’ principle, only permitting interactions with approved entities. For example, a list of IP addresses with normal communication can be kept. If communication is made with an address other than this list, we can generate an alert.
- Long tail log analysis : This method assumes that the behaviors that occur constantly are normal. In other words, if an “Event ID 4624 An account was successfully logged on” log is constantly occurring on a device, with this method we should take it as normal and approach the least occurring logs with suspicion.
Top SIEM vendors in the market
- Wazuh
- IBM Security QRadar
- Splunk Enterprise Security
- LogRhythm NextGen SIEM Platform
- Elastic Security
“To beat a hacker, you have to think like a hacker” 💙
![]()



